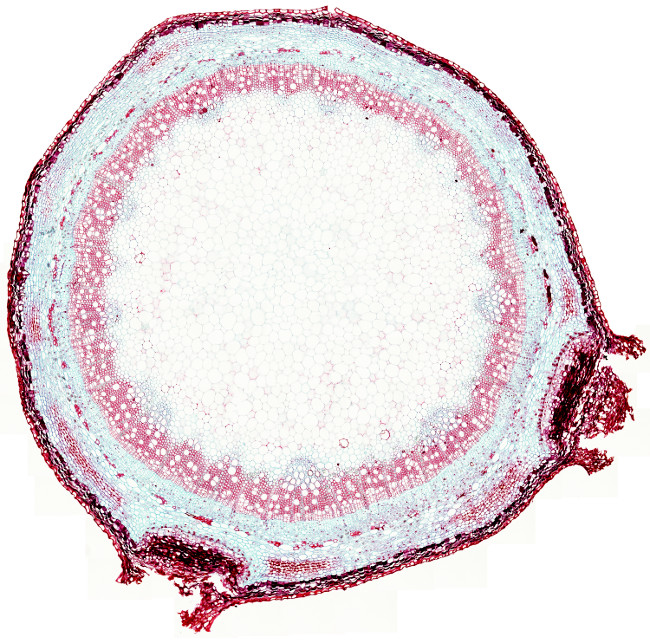
The picture above is from an elder stem undergoing secondary growth. From the surface to the inner regions, the following parts can be distinguished:
Periderm. It is the protecting structure of the stem during secondary growth. In the image above, some epidermis is still remaining (the most supericial layer of cells), which was formed during primary growth. Periderm consists of three layers: the outer phellem, phellogen (cork cambium) and and the inner phelloderm (see this figure).
Cortical parenchyma and collenchyma. The cortical parenchyma is found below the epidermis. In the cortical parenchyma, some regions with lamellar collenchyma are observed. Collenchyma cells show reddish cell walls, whereas parenchyma cells have bluish cell walls. Collenchyma cells have very thick primary cell walls that catch the safranin dye. Parenchyma cells have thinner cell walls stained with blue Alcian dye.
Lenticels. They are found at the surface of the stem as interruptions of the periderm. The main function of lenticels is to allow the exchange of gases between the internal tissues and the atmosphere.
Vascular tissue. Secondary phloem is found below the cortical parenchyma. In this image, the primary phloem is not visible, but it is positioned between the secondary phloem and the cortical parenchyma. Secondary phloem forms a ring in the stem (a cylinder in 3D view) with cells showing thin primary cell walls stained in blue (Alcian blue dye). Secondary xylem is inner to the secondary phloem, and it is stained in red (safranin dye) because their cells have secondary cell walls with lignin. Both, secondary xylem and secondary phloem are differentiated from the vascular cambium, a two thick-cell layer meristem found between them. The vascular cambium is hardly visible in this image. In the inner part of the secondary xylem there are small pyramids of tissue pointing to the center of the stem. They are primary xylem bundles that remain there since the primary growth period of the stem.
Pith or medullary parenchyma is found below the xylem. In this image, pith occupies most stem and it is formed of large cells with thin cell walls stained with blue Alcian.