Animal tissues
Connective tissue proper
MESENCHYMA
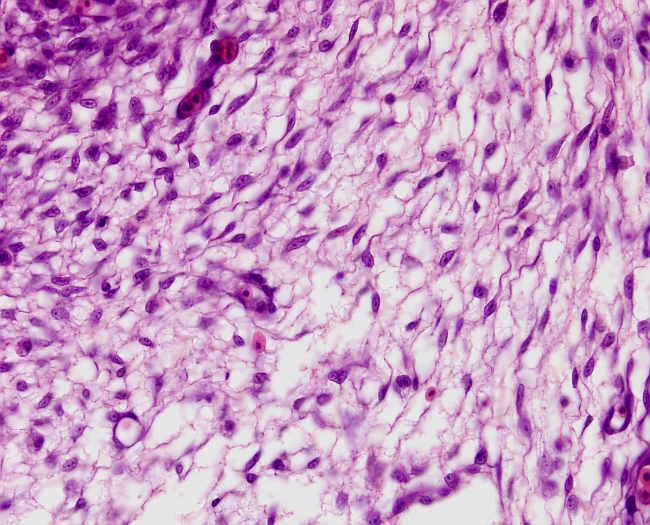
Species: chick (Gallus gallus; bird)
Technique: 8 µm thick paraffin sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin.
Mesenchymal connective tissue is clearly distinguished from other connective tissues by the undifferentiated aspect of its cells, which are known as mesenchymal cells. It also shows abundant and low dense extracellular matrix. Cells are scattered and send thin and long and thin extensions that make contacts between adjoining cells, forming a kind of reticular net. The nucleus is large, with invaginated nuclear envelope, and well-visible nucleolus. In the embryo, mesenchymal tissue extracellular matrix is initially highly fluid because it is mainly made up of ground substance (proteoglycans, glycosaminoglycans, and glycoproteins), but the fibrous part (collagen, elastic fibers, reticular fibers) increases progressively during development.