Animal tissues.
Glandular epithelium.
SALIVARY GLAND
Species: mouse (Mus musculus; mammal).
Technique: 8 µm thick sections stained with haematoxylin-eosin.
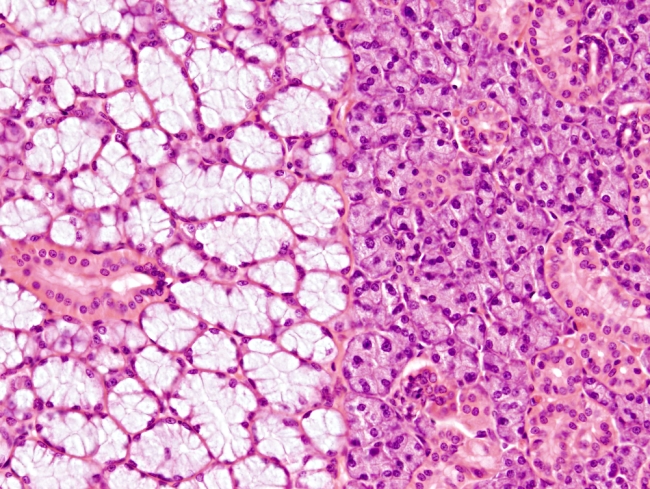
Exocrine glands can be classified according to the type of products they release. Salivary glands are exocrine glands that produce and release saliva. They may contain two types of secretory cells: mucous and serous, that form mucous and serous acini, respectively. Mixed acini with both serous and mucous cells can also be found (see figure 1). Mucous secretory cells show clear cytoplasm because they mostly contain mucopolysaccharides, which do not retain common dyes, and a basal flattened nucleus. Serous secretory cells show a darker cytoplasm due to the high enzymatic content, with amylases as the most abundant enzymes. The nucleus is located in a central position and is rounded. Myoepithelial cells, showing a narrow cytoplasm and a very flattened nucleus, can be found wrapping excretory ducts and some acini. These cells can make contractile movements, which help to expel the gland content.
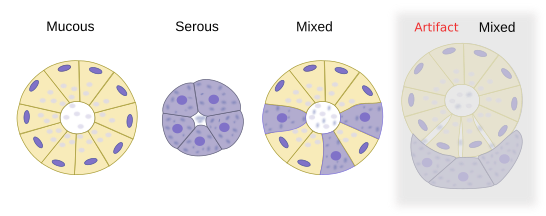
In humans, there are several types of salivary glands: parotid, sublingual, submaxilar and accessory salivary glands, which are smaller and scattered. Only sublingual and submaxilary can release both mucous and serous substances. They are mixed glands. Small salivary glands are mucous. All salivary gland release their content into the oral cavity after the stimulation by the autonomous system.
Más imágenes
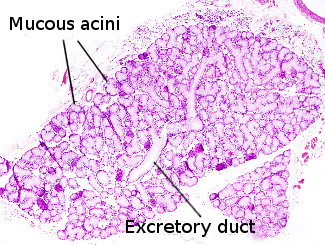
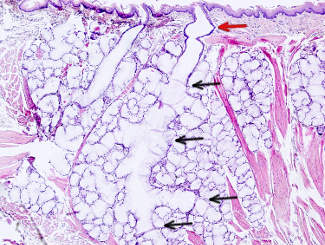

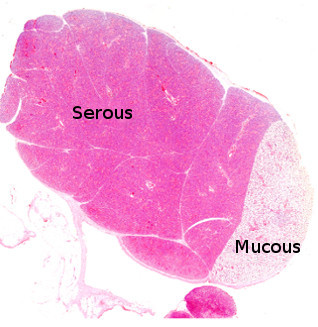

 This image is from rat submaxilar salivary gland.
This image is from rat submaxilar salivary gland.