Atlas of plant and animal histology
Animal tissues.
Connective. Bone.
BONE CELLS
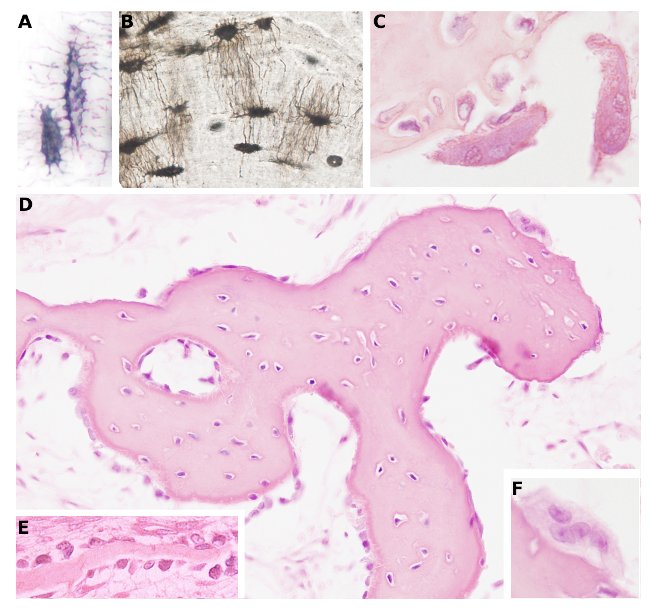
Species: several
Technique: A, B) Abrade surfaces. C-F) Decalcification, hematoxylin and eosin.
The image A is by D. Santiago Gómez Salvador, Dept. Anatomical Pathology, Faculty of Medicine, University of Cádiz. Spain.
Synthesis, degradation, and bone maintenance are carried out by three types of cells.
Osteoblasts(figures D and E) are cells involved in bone matrix synthesis and are responsible for bone growth and remodeling. They synthesize new bone matrix on the external surface of growing bone (see figure E), where they form one cell-thick layer. Osteoblasts are rounded and contain a well-visible nucleus located away from the surface of the bone matrix. As they synthesize extracellular matrix they become more columnar, are more basophilic, whereas they are more flattened if the synthesis rate decreases. The activity of osteoblasts is influenced by the parathyroid hormone.
Osteocytes are the most abundant type of cell in the mature bone. They are found in cavities of the bone matrix, known as bone lacunae. As shown in figures A and B, osteocytes look like spiders with long legs. Those legs are channels, called canaliculi, that extend through the bone matrix. Osteocyte processes run inside these channels allowing the communication of nearby osteocytes. Canaliculi are formed during the differentiation from osteoblasts to osteocytes. Osteocytes are completely surrounded by bone matrix, as shown in figure D.
Osteoclasts are responsible for removing mineralized and organic bone matrix through a process called resorption. As shown in figures C, D and F, osteoclasts are very large and multinucleated cells. In figure C, it can be observed the waved shape of the osteoclast surface facing the bone surface, showing numerous and densely packed folds. This arrangement of the osteoclast surface appears during bone resorption and contains many enzymes that degrade bone matrix.

 The images are from spongy bone.
The images are from spongy bone.