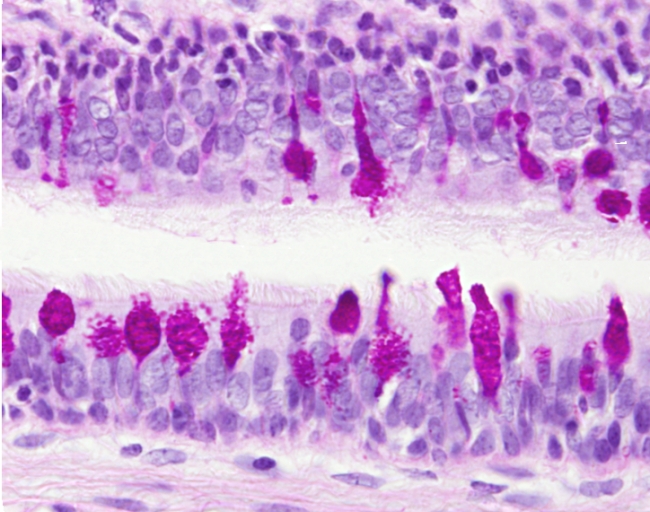
Globet cells (or caliciform cells) are intraepithelial glandular cells scattered in the covering epithelium of the intestine (small and large intestine), and larger respiratory ducts (trachea and bronchi). Globet cells resemble a calyx, with the apical part wider than the basal one. The nucleus is located in the basal part and the secretory vesicles are located toward the apical part (stained in redish in this image). The release of the secretory products is by merocrine secretion. After every secretion event, globet cells become thinner and begin to synthesize new molecules to be released in the next secretion event. The time between two releases is around 1 or 2 hours.
In some places, intraepithelial glandular cells form groups known as intraepithelial glands, which are completely included in the epithelium (see images below). Intraepithelial glands can be found in the nasal cavity, Eustachian ducts, urethra, eyelid and in the eye conjunctive.


