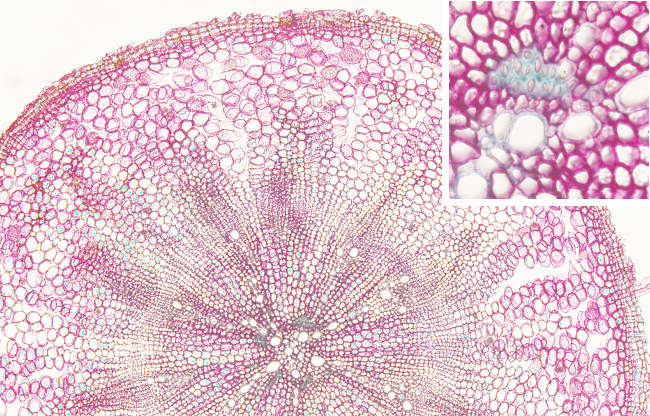
Transversal section of a secondary root of a dicot plant. In the surface, the epidermis is started to be transformed in periderm, with cells showing suberized cells, but with not much suberization yet. Below, the cortex is made up of parenchyma cells with large intercellular spaces. The vascular cambium (not indicated) is a continuous cylinder between the secondary phloem and the secondary xylem. This meristem produces secondary phloem outward and secondary xylem inward. The primary phloem is in the outer surface of the secondary phloem, whereas the primary xylem is in the inner surface of the secondary xylem. Between the secondary xylem tracheae (the large xylem cells) there are parenchyma medullary rays. Small groups of sclerenchyma cells are found delimiting the primary xylem.