Animal tissues. Muscle.
SMOOTH MUSCLE
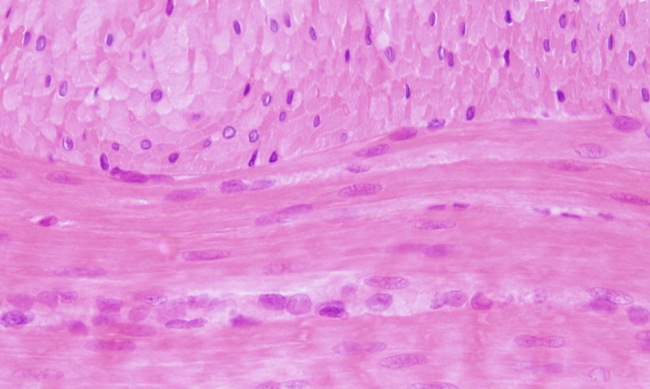
Smooth muscle: muscle layer of the small intestine.
Species: mouse (Mus musculus; mammal).
Technique: haematoxylin and eosin, 8 µm thick section, paraffin embedding.
Species: mouse (Mus musculus; mammal).
Technique: haematoxylin and eosin, 8 µm thick section, paraffin embedding.
Cursor over the mouse to see where the image comes from.
The smooth muscle of the small intestine is shown in this figure. In the upper part, the smooth muscle are observed in a transverse view, whereas in the lower part smooth muscle cells are oriented parallel to the section plane. Smooth muscle cells are fusiform, small in diameter, and with a nucleus adapted to the morphology of the cell. They are non branched cells. Unlike the skeletal and cardiac muscle cells, striations are not observed in the cytoplasm. This is because the cytoskeletal filaments, actin and myosin, are not arranged so regularly, but more scattered. That is why the cytoplasm shows a homogeneous pink staining.
More images
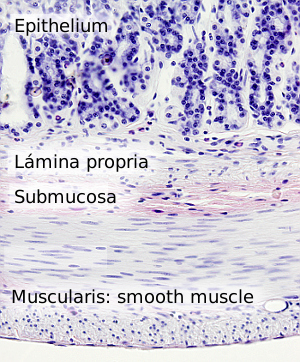
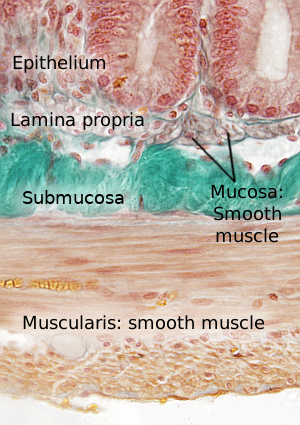

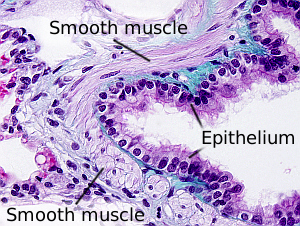
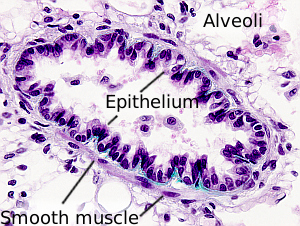

 The image is from small intestine.
The image is from small intestine.