Animal tissues. Epithelium.
SIMPLE SQUAMOUS
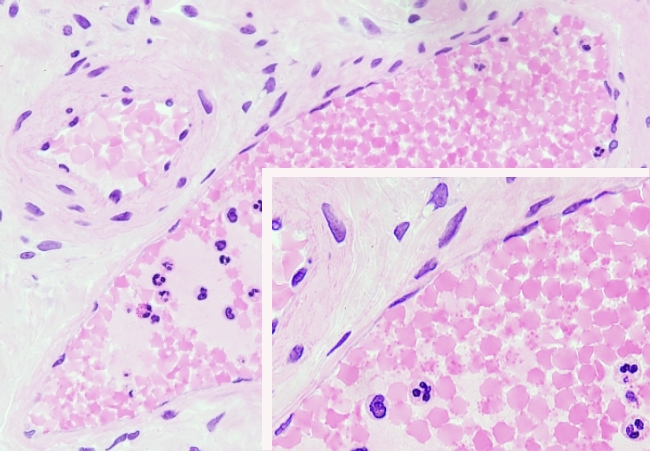
Species: mouse (Mus musculus; mammal)
Staining: 8 µm paraffin sections stained with hematoxylin and eosin.
Across section of two blood vessels, an artery and a vein, is shown in this image. The Boxed image, bottom right, is a magnification of the vein. The inner wall of blood vessels is covered by a simple squamous epithelium known as endothelium (see also figure 1). Epithelial nuclei, although very flattened, are the highest part of endothelium. The cytoplasm is very thin and difficult to observe. Within the blood vessels, erythrocytes and some white blood cells are observed (nucleated blood cells). The endothelial cells show a similar morphology, so it looks like a single cell type. However, depending on the location of the blood vessel in the body, or if it is a capillary or a larger blood vessel, the endothelial cells are functionally different and may contain sets of different molecules.
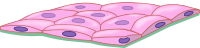
The squamous simple epithelium is made of just one layer of cells, which show a fusiform shape in transverse view, and they look like fried eggs when observed from the top. Epithelial cells are attached to one another by large protein complexes known as cell junctions, mainly tight junctions. They force molecules to cross the epithelium through the cell, instead of through the intercellular spaces. This type of epithelium is found lining surfaces involved in the exchange of molecules.
The main function of this epithelium is to facilitate diffusion and transport of gases and substances across itself. Usually, one of the surfaces of the epithelium is facing a cavity or the lumen of an internal duct of the body. For example, it allows the interchange of gas in the pulmonary alveoli, facilitates the crossing of the mesothelium by internal fluids, the endothelium makes possible the interchange of molecules between blood (as well as lymph) and surrounding tissues, forms the Henle's loop where the major part of the kidney filtration occurs, etcetera.
More pictures
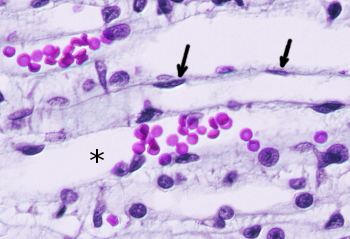
 Pulmonary alveoli are lined by simple squamous epithelium (arrows).
Pulmonary alveoli are lined by simple squamous epithelium (arrows).
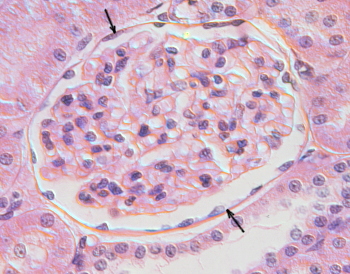
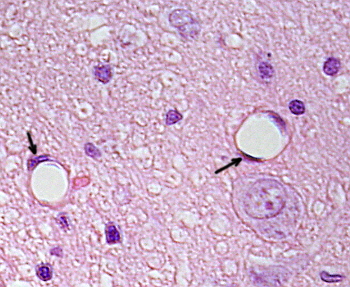 The endothelium (arrows) of a capillary.
The endothelium (arrows) of a capillary.
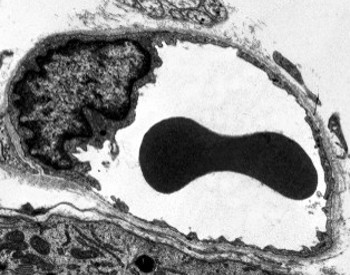 Transmission electron microscopy image of a capillary in transverse view. Simple squamous epithelium forms the wall of the capillary. The endothelial cell cytoplasm is very thin and the nucleus is the widest part of the cell. An erythrocyte is observed inside the capillary.
Transmission electron microscopy image of a capillary in transverse view. Simple squamous epithelium forms the wall of the capillary. The endothelial cell cytoplasm is very thin and the nucleus is the widest part of the cell. An erythrocyte is observed inside the capillary.
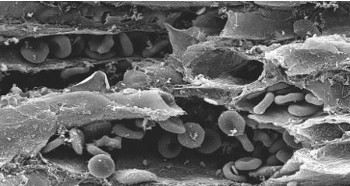 Scanning electron microscopy image showing capillaries with some erythrocytes inside. The walls of capillaries are made up of simple squamous epithelium.
Scanning electron microscopy image showing capillaries with some erythrocytes inside. The walls of capillaries are made up of simple squamous epithelium.